Using SSL/TLS to encrypt a connection to a DB instance or cluster
You can use Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) from your application to encrypt a connection to a database running Db2, MariaDB, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, or PostgreSQL.
Certificate authorities
The certificate authority (CA) is the certificate that identifies the root CA at the top of the certificate chain. The CA signs the DB server certificate, which is installed on each DB instance. The DB server certificate identifies the DB instance as a trusted server.
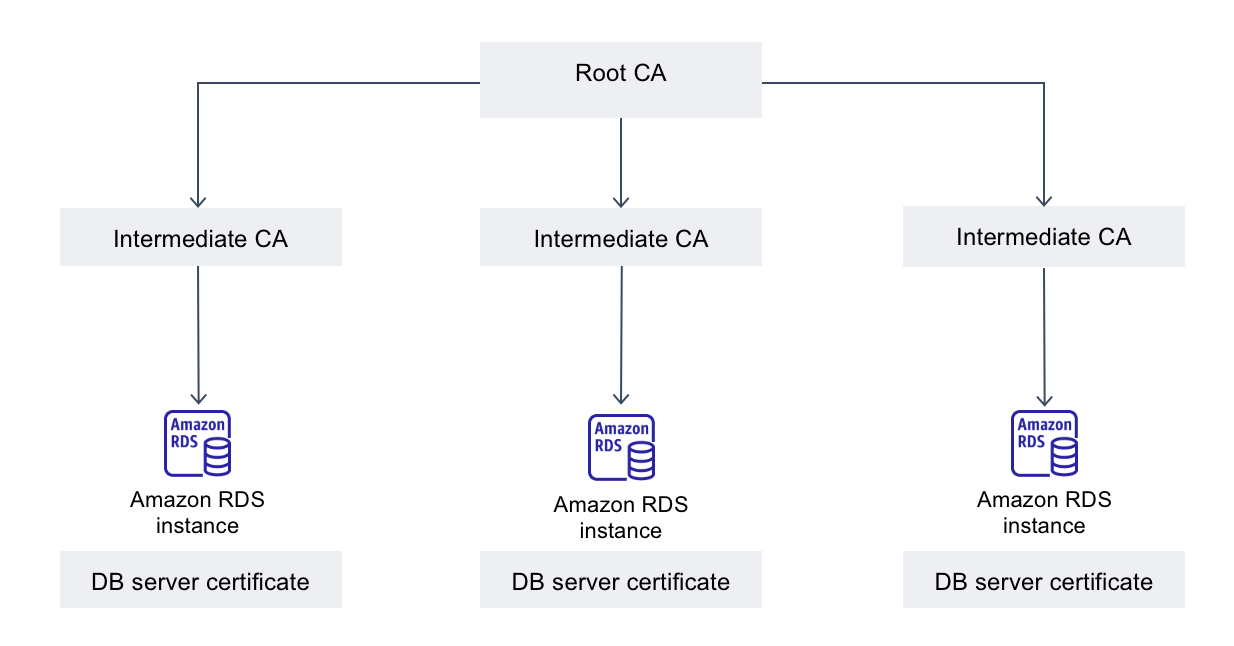
Amazon RDS provides the following CAs to sign the DB server certificate for a database.
| Certificate authority (CA) | Description | Common name (CN) |
|---|---|---|
|
rds-ca-rsa2048-g1 |
Uses a certificate authority with RSA 2048 private key algorithm and SHA256 signing algorithm in most AWS Regions. This CA supports automatic server certificate rotation. |
Amazon RDS region-identifier Root CA RSA2048 G1 |
|
rds-ca-rsa4096-g1 |
Uses a certificate authority with RSA 4096 private key algorithm and SHA384 signing algorithm. This CA supports automatic server certificate rotation. |
Amazon RDS region-identifier Root CA RSA4096 G1 |
|
rds-ca-ecc384-g1 |
Uses a certificate authority with ECC 384 private key algorithm and SHA384 signing algorithm. This CA supports automatic server certificate rotation. |
Amazon RDS region-identifier Root CA ECC384 G1 |
Note
If you are using the AWS CLI, you can see the validities of the certificate authorities listed above by using describe-certificates.
These CA certificates are included in the regional and global certificate bundle. When you use the rds-ca-rsa2048-g1 CA with a database, RDS manages the DB server certificate on the database. RDS rotates the DB server certificate automatically before it expires.
Setting the CA for your database
You can set the CA for a database when you perform the following tasks:
-
Create a DB instance or Multi-AZ DB cluster – You can set the CA when you create a DB instance or cluster. For instructions, see Creating an Amazon RDS DB instance or Creating a Multi-AZ DB cluster for Amazon RDS .
-
Modify a DB instance or Multi-AZ DB cluster – You can set the CA for a DB instance or cluster by modifying it. For instructions, see Modifying an Amazon RDS DB instance or Modifying a Multi-AZ DB cluster for Amazon RDS .
Note
You can override the default CA for your AWS account by using the modify-certificates command.
The available CAs depend on the DB engine and DB engine version. When you use the AWS Management Console, you can choose the CA using the Certificate authority setting, as shown in the following image.
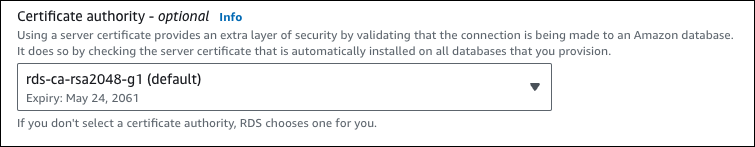
The console only shows the CAs that are available for the DB engine and DB engine version. If you're using the AWS CLI, you can set the CA for a DB instance using the create-db-instance or modify-db-instance command. You can set the CA for a Multi-AZ DB cluster using the create-db-cluster or modify-db-cluster command.
If you're using the AWS CLI, you can see the available CAs for your
account by using the describe-certificates command. This command also shows the
expiration date for each CA in ValidTill in the output. You
can find the CAs that are available for a specific DB engine and DB
engine version using the describe-db-engine-versions command.
The following example shows the CAs available for the default RDS for PostgreSQL DB engine version.
aws rds describe-db-engine-versions --default-only --engine postgres
Your output is similar to the following. The available CAs are listed
in SupportedCACertificateIdentifiers. The output also shows
whether the DB engine version supports rotating the certificate without
restart in
SupportsCertificateRotationWithoutRestart.
{
"DBEngineVersions": [
{
"Engine": "postgres",
"MajorEngineVersion": "13",
"EngineVersion": "13.4",
"DBParameterGroupFamily": "postgres13",
"DBEngineDescription": "PostgreSQL",
"DBEngineVersionDescription": "PostgreSQL 13.4-R1",
"ValidUpgradeTarget": [],
"SupportsLogExportsToCloudwatchLogs": false,
"SupportsReadReplica": true,
"SupportedFeatureNames": [
"Lambda"
],
"Status": "available",
"SupportsParallelQuery": false,
"SupportsGlobalDatabases": false,
"SupportsBabelfish": false,
"SupportsCertificateRotationWithoutRestart": true,
"SupportedCACertificateIdentifiers": [
"rds-ca-rsa2048-g1",
"rds-ca-ecc384-g1",
"rds-ca-rsa4096-g1"
]
}
]
}DB server certificate validities
The validity of DB server certificate depends on the DB engine and DB engine version. If the DB engine version supports rotating the certificate without restart, the validity of the DB server certificate is 1 year. Otherwise the validity is 3 years.
For more information about DB server certificate rotation, see Automatic server certificate rotation .
Viewing the CA for your DB instance
You can view the details about the CA for a database by viewing the Connectivity & security tab in the console, as in the following image.
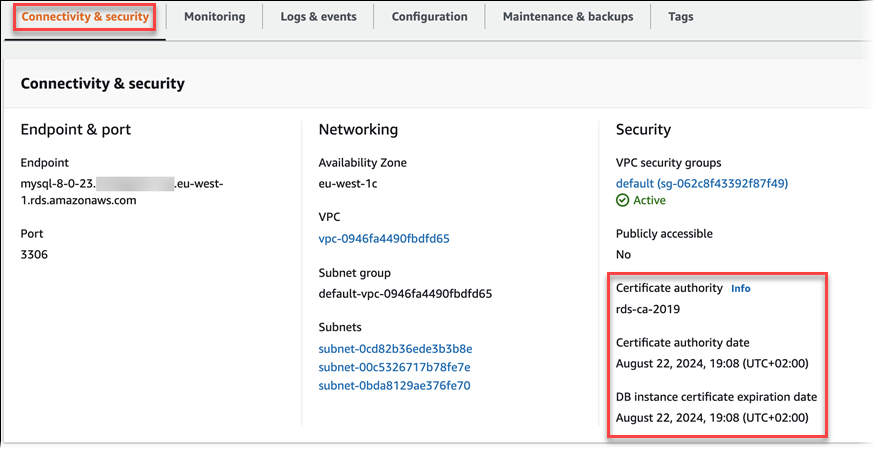
If you're using the AWS CLI, you can view the details about the CA for a DB instance by using the describe-db-instances command. You can view the details about the CA for a Multi-AZ DB cluster by using the describe-db-clusters command.
Download certificate bundles for Amazon RDS
When you connect to your database with SSL or TLS, the database instance requires a trust certificate from Amazon RDS. Select the appropriate link in the following table to download the bundle that corresponds with the AWS Region where you host your database.
Certificate bundles for specific AWS Regions
To get a certificate bundle for the AWS Region, download it from
https://s3.eusc-de-east-1.amazonaws.eu/rds-truststore/eusc-de-east-1/eusc-de-east-1-bundle.pem
If your application is on the Microsoft Windows platform and requires a PKCS7 file, you can download
the PKCS7 certificate bundle that contains both the intermediate and root certificates
at
https://s3.eusc-de-east-1.amazonaws.eu/rds-truststore/eusc-de-east-1/eusc-de-east-1-bundle.p7b
The bundle contains the root CA certificates required for SSL/TLS connections to RDS databases. Your application trust store only needs to register the root CA certificate.
Viewing the contents of your CA certificate
To check the contents of your CA certificate bundle, use the following command:
keytool -printcert -v -file global-bundle.pem